The Backbone Of Mobile Communication
GSM structure is a crucial aspect of mobile communication that has transformed the way we connect with each other. As one of the most widely adopted mobile communication standards globally, GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) provides a framework that enables millions of users to communicate seamlessly. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of GSM structure, exploring its components, functionalities, and significance in the modern telecommunications landscape.
The advent of GSM technology has revolutionized mobile telephony by offering enhanced voice quality, greater network capacity, and improved security features. Understanding the GSM structure is essential for grasping how mobile communication operates and the factors contributing to its success. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of GSM structure while adhering to the principles of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
Join us as we explore the components of GSM structure, its operational principles, and its impact on the telecommunications industry. Whether you are a telecommunications professional, an enthusiast, or simply curious about how mobile communication works, this article will equip you with valuable insights into the world of GSM.
Table of Contents
Biographical Overview of GSM
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) was developed in the late 1980s as a standard for mobile telephony. It was first introduced in Europe and has since become the dominant mobile communication standard worldwide. The GSM standard was established by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and has undergone various upgrades and enhancements over the years.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduced | 1982 |
| Developed by | European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) |
| Frequency Bands | 900 MHz, 1800 MHz |
| Technology Type | 2G Digital Mobile Phone Standard |
| Key Features | Digital transmission, SIM card, roaming capabilities |
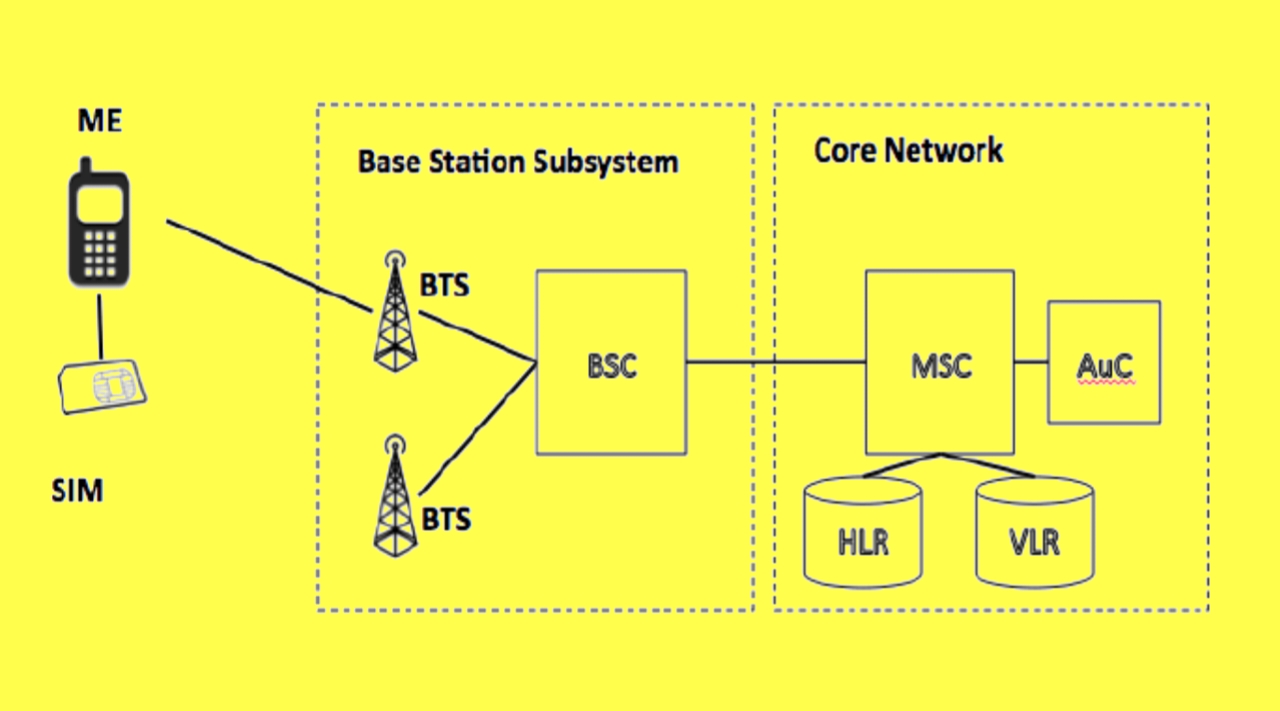
Key Components of GSM Structure
The GSM structure comprises several key components that work in harmony to facilitate mobile communication. Understanding these components is essential for grasping how GSM operates. The primary components include:
- Mobile Station (MS): The user's mobile device, which includes the mobile equipment and SIM card.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): Comprises the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC), responsible for managing radio communication with mobile stations.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): Manages call processing and routing, including the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), which connects calls to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
- Operation Support Subsystem (OSS): Provides network management and maintenance functionalities.
Mobile Station (MS)
The Mobile Station is the end-user device that connects to the GSM network. It consists of two main elements:
- Mobile Equipment (ME): The physical device, such as a smartphone or feature phone.
- Subscriber Identity Module (SIM): A smart card that securely stores the user's subscription information and allows access to the network.
Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
The Base Station Subsystem plays a critical role in managing communication between the mobile station and the network. It includes:
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): Responsible for radio communication with mobile devices.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): Manages multiple BTSs and handles resource allocation and handover processes.
How GSM Works
GSM operates on a digital communication framework, enabling efficient voice and data transmission. The fundamental working principles of GSM include:
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA): Divides the frequency channel into time slots, allowing multiple users to share the same channel.
- Frequency Hopping: Increases security and reduces interference by rapidly changing frequencies during a call.
- Call Setup and Termination: Involves signaling between the mobile station and the network to establish and terminate calls.
GSM Network Architecture
The GSM network architecture is organized into several layers, each serving specific functions. The main components of the architecture include:
- Mobile Station (MS): User's mobile device.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): Manages radio communications.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): Handles call routing and processing.
- Operation Support Subsystem (OSS): Manages network operations.
Signaling in GSM
Signaling in GSM is essential for establishing and maintaining communication. It uses a dedicated signaling system called Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) to manage call setup, routing, and termination.
Handover Process
The handover process allows users to maintain calls while moving between different cells in the network. It can be classified into:
- Hard Handover: The connection to the previous cell is broken before establishing a connection to the new cell.
- Soft Handover: The connection to the new cell is established before disconnecting from the previous cell, providing a seamless transition.
Security Features of GSM
Security is a paramount concern in mobile communication, and GSM incorporates several features to enhance user privacy and data protection:
- Encryption: GSM uses A5 encryption algorithms to secure voice and data transmission.
- Authentication: The network verifies the user's identity using the SIM card's unique identifier.
- Call and SMS Integrity: Ensures the authenticity of messages and calls to prevent tampering.
Evolution of GSM Technology
GSM technology has evolved significantly since its inception, leading to the development of enhanced versions such as:
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service): Introduced data services and improved internet connectivity.
- EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution): Provided faster data rates, enabling multimedia services.
- 3G and Beyond: Transitioned to UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and later to 4G LTE and 5G networks.
Challenges Faced by GSM
Despite its widespread adoption, GSM faces several challenges that impact its performance and security:
- Interference: Signal degradation due to environmental factors and increased user density.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Potential threats from hackers targeting encryption and authentication mechanisms.
- Competition from New Technologies: The rise of 4G and 5G networks poses challenges for the continued relevance of GSM.
The Future of GSM and Mobile Communication
The future of GSM and mobile communication is promising, as ongoing advancements in technology continue to shape the landscape. Key trends include:
- Integration with IoT: GSM technology will play a vital role in connecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Expansion of 5G Networks: The transition to 5G will enhance data speeds and network capacity, impacting
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7o77EnKKepJxjwqx7zaiurKyimq6ug46gqqZlo6m%2Ftq%2FTrqmeZpipuq0%3D
